What is SLA printing, and how can it revolutionize your manufacturing processes? These questions hold the key to unlocking new horizons for your business. This additive manufacturing technology has the potential to redefine the way you create and produce.
SLA, or Stereolithography, is an innovative additive manufacturing technology that is reshaping the manufacturing industry. By utilizing ultraviolet light and photosensitive resin, SLA printing enables the conversion of digital models into tangible objects with unparalleled precision.
Join us as we delve into the intricacies of this groundbreaking technology and uncover its immense potential in modern manufacturing.
1. An Overview of SLA Printing
In my observation, unlike traditional manufacturing methods that rely on removing material to create an object, SLA is additive. According to Science Direct, among various potential technologies for 3D printing, SLA is the first and oldest, yet it delivers complex geometries and smooth-surfaced objects owing to its high printing resolution and is widely used.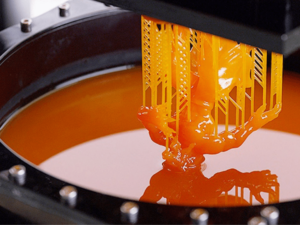
2. How SLA Printing Works: The Basic Principle
SLA printing operates on the basic principle of solidifying resin layers using a UV laser. The choice of resin to work with is critical, and according to LinkedIn, calibration also ensures that the printer operates at its optimal settings. Once the printing is complete, post-processing techniques come into play, all contributing to the enhancement of the final product’s durability and aesthetic appeal.

3. Advantages of SLA Printing
SLA printing offers a myriad of advantages that have revolutionized the manufacturing landscape. Here are some key benefits that make SLA printing an irresistible choice for businesses.
High Resolution and Accuracy
One of the primary advantages of SLA printing is its ability to produce high-resolution and accurate prints. At Suproto, the technology allows for the creation of intricate details, smooth curves, and fine features with exceptional precision. Based from experience, the layer-by-layer approach of SLA printing ensures that each layer is precisely formed, resulting in a final product that closely matches the digital design.
Smooth Surface Finish
SLA printing delivers superior surface quality, characterized by smooth finishes and minimal visible layer lines. For instance, the process of solidifying liquid resin layer by layer allows for the creation of parts with excellent surface aesthetics. The cured resin produces a polished appearance, reducing the need for extensive post-processing and finishing work.
Capability to Print Complex Structures
SLA printing enables the production of complex structures and intricate designs that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. Anyone will agree that the ability to create geometries with overhangs, internal channels, and intricate lattice structures opens up new possibilities for design innovation.
4. The Types of SLA Printing
SLA printing encompasses various techniques, each with its unique characteristics. Understanding the different types below will enable you to make informed decisions for your business needs:
Standard SLA Printing
Standard SLA printing involves using a UV laser to selectively cure liquid resin layer by layer. The UV laser scans the surface of the liquid resin, solidifying it wherever it touches, following the digital design. Amazing, right? Standard SLA printers offer high accuracy and resolution, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from prototyping to small-scale production.

Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Digital Light Processing (DLP) is a variation of SLA printing that uses a digital light projector to cure the entire layer of resin simultaneously. Instead of a laser, a digital micromirror device (DMD) projects a pattern of UV light onto the resin, solidifying it in a single exposure. DLP printing allows for faster printing speeds compared to traditional SLA, making it advantageous for large-scale production and time-sensitive projects.

Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP)
Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP) is a cutting-edge SLA printing technology developed by Carbon. At Suproto, CLIP utilizes a combination of oxygen-permeable optics and a programmable light source to create a “continuous” printing process. Thanks to this process, it enables faster printing speeds while maintaining high-resolution and surface quality.
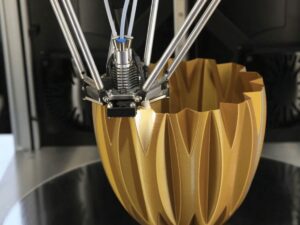
5. Applications of SLA Printing
SLA printing finds applications in diverse industries. Below let us explore some key sectors where SLA printing has made significant contributions:
Manufacturing and Prototyping
In the realm of manufacturing and prototyping, SLA printing has revolutionized the process by enabling rapid iteration and cost-effective production of prototypes. It allows designers and engineers to validate designs, test functionalities, and gather feedback before moving to full-scale production.
Medicine and Dentistry
SLA printing has found widespread use in the medical and dental fields. It allows for the creation of accurate anatomical models, surgical guides, and patient-specific implants. SLA-printed surgical guides aid in precise implant placement, improving surgical outcomes. Dental laboratories leverage SLA printing to produce highly accurate and customized dental models, crowns, and orthodontic appliances.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry benefits from SLA printing for prototyping and functional testing of various components. For example, it enables the production of lightweight and complex parts, such as intake manifolds, engine covers, and interior trim pieces. SLA-printed prototypes allow designers and engineers to assess form, fit, and function early in the design process.
Art and Design
SLA printing has become a game-changer in the world of art and design. Artists and designers leverage their capabilities to create intricate sculptures, architectural models, jewelry, and decorative pieces. The high resolution and smooth surface finish achieved through SLA printing enable the realization of intricate and visually stunning designs that were once difficult to fabricate using traditional methods.
6. Comparing SLA Printing with Other 3D Printing Technologies
When considering the implementation of SLA printing for your business, it’s important to understand how it compares to other 3D printing technologies. Here are some key comparisons between SLA printing and other popular techniques.
SLA vs FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
SLA printing and FDM are two widely used 3D printing technologies, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. While SLA printing excels in producing highly detailed and accurate prints with smooth surface finishes, FDM is known for its affordability and ability to print larger objects. SLA printing is ideal for applications that require high precision and intricate details, such as prototypes, jewelry, and dental models.
SLA vs SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
SLA printing and SLS are both additive manufacturing processes but differ in their approach. SLA uses liquid resin and UV lasers to solidify the layers, while SLS involves the use of powdered materials and a high-power laser to fuse the particles together. In my research, SLA printing offers higher resolution and finer details, making it suitable for intricate designs and small-scale production.
SLA vs PolyJet Technology
PolyJet technology is another popular 3D printing method that shares some similarities with SLA printing. Both technologies offer high-resolution prints with smooth surface finishes. However, there are some notable differences. SLA printing uses a liquid resin that is cured by a UV laser, while PolyJet technology uses liquid photopolymers that are jetted onto a build platform and cured using UV light.
7. Practical Considerations for SLA Printing
While SLA printing offers numerous benefits, it’s important to consider practical aspects to ensure successful implementation. Let’s explore some key considerations for SLA printing.
The Cost Factor
When considering SLA printing, it’s essential to evaluate the overall cost involved. This includes not only the initial investment in the SLA printer but also ongoing expenses such as resin materials, post-processing equipment, and maintenance. Additionally, consider factors like electricity consumption and labor costs associated with pre-printing preparation and post-processing tasks.
Material Choices in SLA Printing
SLA printing offers a wide range of materials, each with its own characteristics and properties. Consider the specific requirements of your project and choose the appropriate resin material accordingly. Factors to consider include mechanical properties, color options, biocompatibility (if applicable), and post-processing requirements.
The following table presents a variety of resin materials commonly used in SLA printing, highlighting their characteristics, mechanical properties, color options, biocompatibility (if applicable), and post-processing requirements.
| Material |
Characteristics and Properties |
Mechanical Properties |
Color Options |
Biocompatibility |
Post-Processing Requirements |
| Standard Resin |
Affordable and versatile resin suitable for general-purpose printing. |
Good strength and moderate flexibility |
Limited color options |
No |
Requires post-curing |
| Flexible Resin |
Rubber-like material with high flexibility and elongation. |
High flexibility and excellent elongation |
Limited color options |
No |
Requires post-curing |
| Tough Resin |
Durable and impact-resistant resin for functional prototypes. |
High impact resistance and stiffness |
Limited color options |
No |
Requires post-curing |
| High-Temperature Resin |
Resistant to high temperatures, suitable for thermal testing. |
High heat resistance and thermal stability |
Limited color options |
No |
Requires post-curing |
| Transparent Resin |
Clear and translucent resin for applications requiring transparency. |
High transparency and light transmission |
Limited color options |
No |
Requires post-curing and polishing |
| Dental Resin |
Biocompatible resin for dental models and prosthetics. |
Biocompatible and suitable for oral use |
Limited color options |
Yes |
Requires post-curing and polishing |
| Castable Resin |
Resin designed for investment casting. |
High burnout properties and smooth surfaces |
Limited color options |
No |
Requires post-curing and casting |
| Ceramic Resin |
Resin that can be fired to produce ceramic-like objects. |
High-temperature resistance and ceramic finish |
Limited color options |
No |
Requires post-curing and firing |
| Castable Wax Resin |
Resin that can be used for investment casting of metal parts. |
High burnout properties and intricate details |
Limited color options |
No |
Requires post-curing and casting |
Health and Safety Concerns with SLA Printin
While SLA printing is generally safe when proper precautions are taken, it’s important to address any potential health and safety concerns. Resin materials used in SLA printing may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the printing process, so it’s crucial to operate in a well-ventilated area or use appropriate fume extraction systems.
Environmental Impact of SLA Printing
As with any manufacturing process, it’s important to consider the environmental impact of SLA printing. Resin materials used in SLA printing can be hazardous if not properly handled or disposed of. I suggest ensuring proper waste management and disposal practices for used resin, uncured prints, and cleaning solutions. Consider environmentally friendly options and explore recycling methods for waste materials.
8. Buying an SLA Printer: 5 Things to Consider
Investing in an SLA printer requires careful evaluation to choose the right equipment for your business needs. Let’s explore some important factors to consider when purchasing an SLA printer
#1 Understanding the Different Types of SLA Printers
SLA printers come in various models and configurations, each with its own features and capabilities. Research and understand the different types of SLA printers available on the market, such as desktop-sized printers for small-scale operations or industrial-grade printers for larger production volumes. Consider factors such as build volume, resolution, print speed, and compatibility with different resin materials.
#2 Assessing Print Quality and Resolution
Print quality and resolution are critical factors to consider when purchasing an SLA printer. Evaluate the printer’s capabilities in terms of layer thickness, XY resolution, and dimensional accuracy. Trust me, higher resolution printers can produce more intricate details and smoother surface finishes, but they may also come at a higher cost.
#3 Evaluating Material Compatibility
Ensure that the SLA printer you choose is compatible with a wide range of resin materials suitable for your specific applications. Check the availability and compatibility of different resin formulations, including those with specialized properties like high temperature resistance or biocompatibility.
#4 Considering the Total Cost of Ownership
In addition to the initial purchase price of the SLA printer, it’s crucial to consider the total cost of ownership over the printer’s lifespan. Take into account factors such as ongoing maintenance costs, replacement parts, and the cost of consumables like resin and building platform sheets. Additionally, factor in any necessary post-processing equipment and materials.
#5 Checking Vendor Support and Warranty Options
Evaluate the reputation and support offered by the SLA printer manufacturer or vendor. Look for manufacturers with a track record of providing reliable products and excellent customer service. Check the warranty coverage and support options provided. You should be sure that a reputable vendor will offer comprehensive technical support, training resources, and readily available replacement parts.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse product options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available to assist and guide you.
Conclusion
SLA printing offers remarkable capabilities and advantages that have revolutionized modern manufacturing. By comparing SLA printing with other 3D printing technologies, understanding practical considerations, and evaluating factors when buying an SLA printer, businesses can harness the power of this transformative technology to enhance their production processes and drive innovation.
If you are ready to embrace the power of SLA printing, consider partnering with Suproto, a leading manufacturer of state-of-the-art SLA printers. Our expertise and cutting-edge technology can empower your business to unlock new possibilities and stay at the forefront of manufacturing innovation. Contact us today to explore how SLA printing can transform your business.





